Uma matriz é um tamanho fixo, homogêneo estrutura de dados . A limitação dos arrays é que eles têm tamanho fixo. Isso significa que devemos especificar o número de elementos ao declarar o array. Aqui surge uma pergunta: e se quisermos inserir um elemento e não sobrar mais espaço para o novo elemento? Aqui, o conceito de matriz dinâmica passa a existir. Ele gasta o tamanho do array dinamicamente.
Nesta seção, entenderemos o que é um array dinâmico, recursos do array dinâmico, como redimensionar um array dinâmico, e como implementar array dinâmico em Java .
O que é uma matriz dinâmica?
A matriz dinâmica é um tamanho variável estrutura de dados de lista. Ele cresce automaticamente quando tentamos inserir um elemento se não sobrar mais espaço para o novo elemento. Permite-nos adicionar e remover elementos. Ele aloca memória em tempo de execução usando o heap. Ele pode alterar seu tamanho durante o tempo de execução.
Em Java , ListaArray é uma implementação redimensionável. Ele implementa a interface List e fornece todos os métodos relacionados às operações da lista. A força da matriz dinâmica é:
- Pesquisa rápida
- Tamanho variável
- Compatível com cache
Trabalho de matriz dinâmica
Na matriz dinâmica, os elementos são armazenados de forma contígua desde o início da matriz e o espaço restante permanece sem uso. Podemos adicionar os elementos até que o espaçamento reservado seja totalmente consumido. Quando o espaço reservado é consumido e é necessário adicionar alguns elementos. Nesse caso, o tamanho do array de tamanho fixo precisa ser aumentado. Observe que antes de anexar o elemento, alocamos um array maior, copiamos os elementos do array e retornamos o array recém-criado.
Outra maneira de adicionar um elemento é primeiro criar uma função que crie um novo array de tamanho duplo, copie todos os elementos do array antigo e retorne o novo array. Da mesma forma, também podemos diminuir o tamanho da matriz dinâmica.
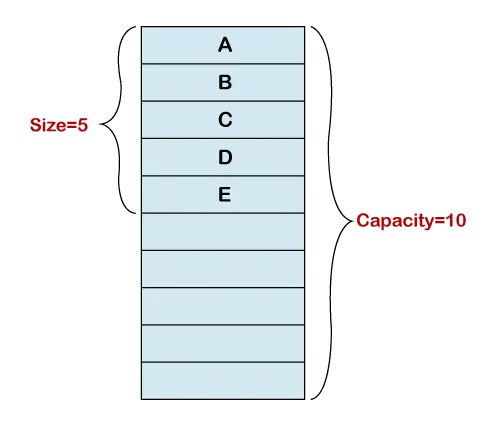
Tamanho vs. Capacidade
A inicialização de um array dinâmico cria um array de tamanho fixo. Na figura a seguir, a implementação do array possui 10 índices. Adicionamos cinco elementos ao array. Agora, a matriz subjacente tem comprimento cinco. Portanto, o comprimento do tamanho do array dinâmico é 5 e sua capacidade é 10. O array dinâmico rastreia o ponto final.
Recursos do array dinâmico
Em Java, o array dinâmico possui três recursos principais: Adicione um elemento, exclua um elemento e redimensione um array.
Adicionar elemento em um array dinâmico
No array dinâmico, podemos criar um array de tamanho fixo se precisarmos adicionar mais alguns elementos ao array. Normalmente, ele cria um novo array de tamanho duplo. Depois disso, ele copia todos os elementos para o array recém-criado. Usamos a seguinte abordagem:

Excluir um elemento de uma matriz dinâmica
Se quisermos remover um elemento do array no índice especificado, usamos o removerAt(i) método. O método analisa o número do índice daquele elemento que queremos excluir. Depois de excluir o elemento, ele desloca os elementos restantes (elementos que estão à direita do elemento excluído) para a esquerda do número de índice especificado. Também usamos o método remove() que exclui um elemento do final do array. Depois de mudar os elementos, ele armazena 0 no palácio do último elemento. Vamos entender através de um exemplo, como mostramos na figura a seguir.

Redimensionando um array dinâmico em Java
Precisamos redimensionar um array em dois cenários se:
- A matriz usa memória extra do que o necessário.
- O array ocupa toda a memória e precisamos adicionar elementos.
No primeiro caso, usamos o SrinkSize() método para redimensionar o variedade . Reduz o tamanho da matriz. Ele libera memória extra ou não utilizada. No segundo caso, usamos o crescerTamanho() método para redimensionar o array. Aumenta o tamanho da matriz.
É uma operação cara porque requer um array maior e copia todos os elementos do array anterior e depois retorna o novo array.

Suponha que no array acima seja necessário adicionar mais seis elementos e, no array, não resta mais memória para armazenar elementos. Nesses casos, aumentamos o array usando o crescerTamanho() método.

Inicialize um array dinâmico
A inicialização do array dinâmico é igual à do array estático. Considere o seguinte programa Java que inicializa um array dinâmico.
InicializarDynamicArray.java
public class InitializeDynamicArray { public static void main(String[] args) { //declaring array int array[]; //initialize an array array= new int[6]; //adding elements to the array array[0] = 34; array[1] = 90; array[2] = 12; array[3] = 22; array[4] = 9; array[5] = 27; System.out.print('Elements of Array are: '); //iteraton over the array for(int i=0; i <array.length ; i++) { system.out.print(array[i] +' '); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Elements of Array are: 34 90 12 22 9 27 </pre> <p>Let's implement the operations in a Java program that we have discussed above.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample1.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + ' '); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println('
elements after adding 5:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println('elements of array:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] ' '); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print('
elements element: system.out.print('no. da.count+'
'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;></pre></array.length> Vamos implementar as operações em um programa Java que discutimos acima.
DynamicArrayExample1.java
public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + \' \'); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println(\'
elements after adding 5:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println(\'elements of array:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] \' \'); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print(\'
elements element: system.out.print(\'no. da.count+\'
\'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;>