Como funcionam os cookies?
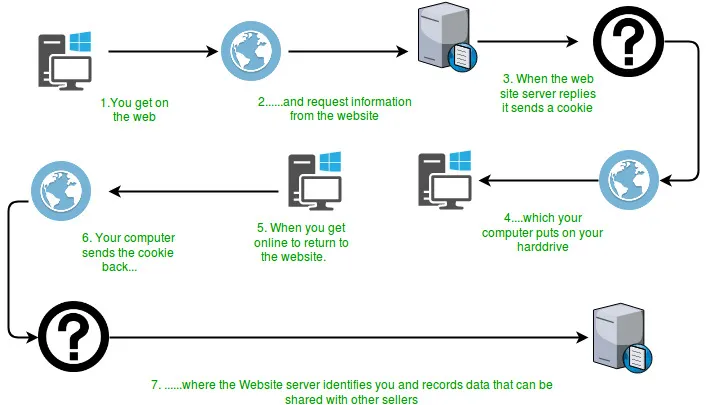 Conforme pode ser visto no diagrama acima, quando um usuário solicita uma página pela primeira vez, o servidor junto com o recurso envia um objeto cookie para ser armazenado na máquina do cliente. Este objeto pode conter detalhes da solicitação. Agora, mais tarde, se o usuário solicitar novamente o mesmo recurso, ele enviará junto com a solicitação o cookie armazenado que poderá ser utilizado pelos servidores para aprimorar ainda mais a experiência do usuário. Atributos do cookie:
Conforme pode ser visto no diagrama acima, quando um usuário solicita uma página pela primeira vez, o servidor junto com o recurso envia um objeto cookie para ser armazenado na máquina do cliente. Este objeto pode conter detalhes da solicitação. Agora, mais tarde, se o usuário solicitar novamente o mesmo recurso, ele enviará junto com a solicitação o cookie armazenado que poderá ser utilizado pelos servidores para aprimorar ainda mais a experiência do usuário. Atributos do cookie: - Primeiro, o servlet define um cookie com o nome test_cookie. Outras linhas do programa definem os atributos do cookie, como valor máximo do domínio, etc.
- Em segundo lugar, o servlet usa request.getCookies para localizar todos os cookies recebidos e exibir seus nomes e outros atributos correspondentes.
- Se nenhum cookie for encontrado, como é o caso da primeira solicitação, uma simples mensagem será exibida informando que esta é a primeira visita à página.
Set-Cookie:session-id = 187-4969589-3049309
Set-Cookie: user = geek ;Domain =.foo.example.com
Set-Cookie: user = geek; Path =/ restricted
Set-Cookie: user = geek; expires = Wed 21-Feb-2017 15:23:00 IST
Set-Cookie: user = 'geek'; Max-Age = 3600Construtor : Creates a cookie with specified name-value pair.
Syntax : public Cookie(String name String value) Parameters : name : name of the cookie value : value associated with this cookieMétodos:
Syntax : public void setDomain(String pattern) Parameters : pattern : string representing the domain in which this cookie is visible.
Syntax : public String getDomain()
Syntax : public void setComment(String purpose) Parameters : purpose : string representing the purpose of this cookie.
Syntax : public String getComment()
Syntax : public void setMaxAge(long time) Parameters : time : time in seconds before this cookie expires
Syntax : public String getMaxAge()
Syntax : public void setPath(String path) Parameters : path : path where this cookie is returned
Syntax : public String getMaxAge()
Syntax : public void setSecure(boolean secure) Parameters: secure - If true the cookie can only be sent over a secure protocol like https. If false it can be sent over any protocol.
Syntax : public boolean getSecure()
Syntax : public String getName()
Syntax : public void setValue(String newValue) Parameters : newValue - a String specifying the new value
Syntax : public String getValue()
Syntax : public int getVersion()
Syntax : public void setVersion(int v) Parameters : v - 0 for original Netscape specification; 1 for RFC 2965/2109
Syntax : public Cookie clone()Below is a Java implementation of a simple servlet program which stores a cookie in the browser when user first requests for it and then for further requests it displays the cookies stored. Java
// Java program to illustrate methods // of Cookie class import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.Cookie; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * Servlet implementation class cookieTest */ @WebServlet('/cookieTest') public class cookieTest extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public cookieTest() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException IOException { response.setContentType('text/html'); // Create a new cookie with the name test cookie // and value 123 Cookie cookie = new Cookie('test_cookie' '123'); // setComment() method cookie.setComment('Just for testing'); // setDomain() method // cookie.setDomain('domain'); // setMaxAge() method cookie.setMaxAge(3600); // setPath() method cookie.setPath('/articles'); // setSecure() method cookie.setSecure(false); // setValue() method cookie.setValue('321'); // setVersion() method cookie.setVersion(0); response.addCookie(cookie); PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter(); pw.print(' '); Cookie ck[] = request.getCookies(); if (ck == null) { pw.print('This is first time the page is requested.
'); pw.print('And therefore no cookies found
'); } else { pw.print('Welcome Again...Cookies found
'); for (int i = 0; i < ck.length; i++) { // getName() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getName() + ''); // getValue() method pw.print('Value :'
+ ck[i].getValue() + ''); // getDomain() method pw.print('Domain :'
+ ck[i].getDomain() + ''); // getPath() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getPath() + ''); // getMaxAge() method pw.print('Max Age :'
+ ck[i].getMaxAge() + ''); // getComment() method pw.print('Comment :'
+ ck[i].getComment() + ''); // getSecure() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getSecure() + ''); // getVersion() method pw.print('Version :'
+ ck[i].getVersion() + ''); } pw.print(' '); } pw.close(); } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException IOException { doGet(request response); } }
This is first time the page is requested. And therefore no cookies found.Para a segunda solicitação:
Welcome Again...Cookies found Name :test_cookie Value :321 Domain :null Name :null Max Age :-1 Comment :null Name :false Version :0
Como executar o programa acima?
Primeiro, certifique-se de ter algum servidor como o Apache Tomcat instalado e configurado com a ferramenta que você está usando, como o Eclipse. Basta executar o programa acima no servidor ou no navegador local, colocando o endereço completo do diretório do servidor que você está usando. O servlet CookieTest é um servlet que executa três tarefas: