Árvore binária é uma estrutura de dados não linear do tipo árvore usada principalmente para classificação e pesquisa porque armazena dados em formato hierárquico. Nesta seção, aprenderemos o implementação de estrutura de dados de árvore binária em Java . Além disso, fornece uma breve descrição da estrutura de dados da árvore binária.
Árvore binária
Uma árvore em que cada nó (pai) possui no máximo dois nós filhos (esquerdo e direito) é chamada de árvore binária. O nó superior é chamado de nó raiz. Em uma árvore binária, um nó contém os dados e o ponteiro (endereço) do nó filho esquerdo e direito.
O altura de uma árvore binária é o número de arestas entre a raiz da árvore e sua folha mais distante (mais profunda). Se a árvore estiver vazio , a altura é 0 . A altura do nó é denotada por h .
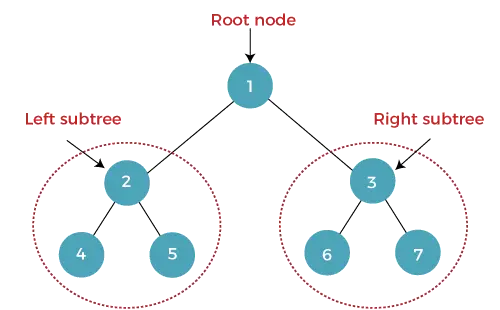
A altura da árvore binária acima é 2.
Podemos calcular o número de folhas e nós usando a seguinte fórmula.
- O número máximo de nós folha é uma árvore binária: 2h
- O número máximo de nós é uma árvore binária: 2h+1-1
Onde h é a altura da árvore binária.
Exemplo de árvore binária

Tipos de árvore binária
Existem os seguintes tipos de árvore binária na estrutura de dados:
- Árvore completa/estritamente binária
- Árvore binária completa
- Árvore Binária Perfeita
- Equilibrar árvore binária
- Árvore binária enraizada
- Árvore binária degenerada/patológica
- Árvore Binária Estendida
- Árvore binária distorcida
- Árvore binária inclinada para a esquerda
- Árvore binária inclinada para a direita
- Árvore binária encadeada
- Árvore binária de thread único
- Árvore Binária de Rosca Dupla
Implementação de árvore binária em Java
Existem muitas maneiras de implementar a árvore binária. Nesta seção, implementaremos a árvore binária usando a estrutura de dados LinkedList. Junto com isso, também implementaremos as ordens de travessia, pesquisando um nó e inserindo um nó em uma árvore binária.
objeto para jsonobject java
Implementação de árvore binária usando LinkedList
Algoritmo
Defina a classe Node que contém três atributos, a saber: dados esquerdo e direito. Aqui, a esquerda representa o filho esquerdo do nó e a direita representa o filho direito do nó.
- Quando um nó é criado, os dados passarão para o atributo de dados do nó e tanto a esquerda quanto a direita serão definidas como nulas.
- Defina outra classe que possua um atributo raiz.
- Root representa o nó raiz da árvore e inicializa-o como nulo.
- Verifica se a raiz é nula, o que significa que a árvore está vazia. Ele adicionará o novo nó como root.
- Caso contrário, adicionará root à fila.
- A variável node representa o nó atual.
- Primeiro, ele verifica se um nó possui filhos esquerdo e direito. Se sim, adicionará ambos os nós à fila.
- Se o filho esquerdo não estiver presente, o novo nó será adicionado como filho esquerdo.
- Se o esquerdo estiver presente, o novo nó será adicionado como o filho direito.
- Ele percorre toda a árvore e imprime o filho esquerdo seguido pela raiz e depois pelo filho direito.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } Saída:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Operações de árvore binária
As seguintes operações podem ser realizadas em uma árvore binária:
- Inserção
- Eliminação
- Procurar
- Travessia
Programa Java para inserir um nó na árvore binária
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } Saída:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Programa Java para excluir um nó em Java
Algoritmo
- Começando na raiz, encontre o nó mais profundo e mais à direita na árvore binária e o nó que queremos excluir.
- Substitua os dados do nó mais à direita pelo nó a ser excluído.
- Em seguida, exclua o nó mais profundo à direita.
Considere a figura a seguir.

ExcluirNode.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } Saída:
opa
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
Programa Java para pesquisar um nó na árvore binária
Algoritmo
- Defina a classe Node que possui três atributos, a saber: dados esquerdo e direito. Aqui, a esquerda representa o filho esquerdo do nó e a direita representa o filho direito do nó.
- Quando um nó é criado, os dados passarão para o atributo de dados do nó e tanto a esquerda quanto a direita serão definidas como nulas.
- Defina outra classe que tenha dois atributos root e flag.
- Root representa o nó raiz da árvore e o inicializa como nulo.
- O Flag será usado para verificar se determinado nó está presente na árvore ou não. Inicialmente, será definido como falso.
- Verifica se a raiz é nula, o que significa que a árvore está vazia.
- Se a árvore não estiver vazia, ela comparará os dados temporários com o valor. Se forem iguais, o sinalizador será definido como verdadeiro e retornará.
- Percorra a subárvore esquerda chamando searchNode() recursivamente e verifique se o valor está presente na subárvore esquerda.
- Percorra a subárvore direita chamando searchNode() recursivamente e verifique se o valor está presente na subárvore direita.
PesquisaBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } Saída:
Element is present in the binary tree.
Travessia de árvore binária
| Ordem transversal | Primeira visita | Segunda visita | Terceira Visita |
|---|---|---|---|
| Em ordem | Visite a subárvore esquerda em ordem | Visite o nó raiz | Visite a subárvore direita em ordem |
| Pedido antecipado | Visite o nó raiz | Visite a subárvore esquerda na encomenda | Visite a subárvore direita na pré-encomenda |
| Encomenda por correio | Visite a subárvore esquerda em pós-ordem | Visite a subárvore direita em pós-ordem | Visite o nó raiz |
Nota: Exceto as três travessias acima, há outra ordem de travessia chamada travessia de limite.
Programa Java para percorrer travessia em ordem, pré-encomenda e pós-ordem
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } Saída:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
Além das operações acima, também podemos realizar operações como nó grande, nó menor e soma de todos os nós.
Programa Java para encontrar o maior nó na árvore binária
MaiorNode.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } Saída:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
Programa Java para encontrar o menor nó na árvore binária
Algoritmo
- Defina a classe Node que possui três atributos, a saber: dados, esquerda e direita. Aqui, a esquerda representa o filho esquerdo do nó e a direita representa o filho direito do nó.
- Quando um nó é criado, os dados passarão para o atributo de dados do nó e tanto a esquerda quanto a direita serão definidas como nulas.
- Defina outra classe que possua um atributo raiz.
Raiz representa o nó raiz da árvore e inicializa-o como nulo.
- Ele verifica se raiz é nula , o que significa que a árvore está vazia.
- Se a árvore não estiver vazia, defina uma variável min que armazenará os dados temporários.
- Descubra o nó mínimo na subárvore esquerda chamando menorElement() recursivamente. Armazene esse valor em leftMin. Compare o valor de min com leftMin e armazene o mínimo de dois em min.
- Descubra o nó mínimo na subárvore direita chamando menorElement() recursivamente. Armazene esse valor em rightMin. Compare o valor de min com rightMin e armazene o máximo de dois em min.
- No final, min conterá o menor nó da árvore binária.
MenorNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } Saída:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
Programa Java para encontrar a largura máxima de uma árvore binária
Algoritmo
- Defina a classe Node que possui três atributos, a saber: dados esquerdo e direito. Aqui, a esquerda representa o filho esquerdo do nó e a direita representa o filho direito do nó.
- Quando um nó é criado, os dados passarão para o atributo de dados do nó e tanto a esquerda quanto a direita serão definidas como nulas.
- Defina outra classe que possua um atributo raiz.
Raiz representa o nó raiz da árvore e o inicializa como nulo.
- A variável maxWidth armazenará o número máximo de nós presentes em qualquer nível.
- A fila é usada para percorrer o nível da árvore binária.
- Verifica se a raiz é nula, o que significa que a árvore está vazia.
- Caso contrário, adicione o nó raiz à fila. A variável nodesInLevel controla o número de nós em cada nível.
- Se nodesInLevel > 0, remova o nó da frente da fila e adicione seus filhos esquerdo e direito à fila. Para a primeira iteração, o nó 1 será removido e seus nós filhos 2 e 3 serão adicionados à fila. Na segunda iteração, o nó 2 será removido, seus filhos 4 e 5 serão adicionados à fila e assim por diante.
- MaxWidth armazenará max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel). Portanto, em qualquer momento, representará o número máximo de nós.
- Isso continuará até que todos os níveis da árvore sejam percorridos.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } Saída:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
