O loop for em linguagem C é usado para iterar as instruções ou parte do programa várias vezes. É freqüentemente usado para percorrer estruturas de dados como array e lista vinculada.
Sintaxe do loop for em C
A sintaxe do loop for em linguagem c é fornecida abaixo:
convertendo objeto em string
for(Expression 1; Expression 2; Expression 3){ //code to be executed } Fluxograma do loop for em C
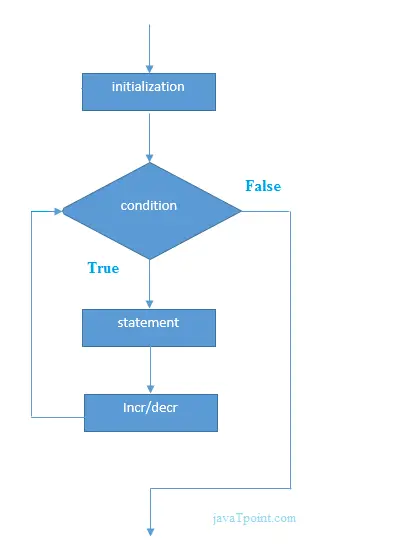
C para exemplos de loop
Vamos ver o programa simples do loop for que imprime a tabela de 1.
#include int main(){ int i=0; for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',i); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 </pre> <h3>C Program: Print table for the given number using C for loop</h3> <pre> #include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf('%d ',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf('%d %d %d
',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf('%d %d
',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){></pre></=10;i++){> Programa C: Imprimir tabela para o número fornecido usando C for loop
#include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf(\'%d
\',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
Propriedades da Expressão 1
- A expressão representa a inicialização da variável de loop.
- Podemos inicializar mais de uma variável na Expressão 1.
- A expressão 1 é opcional.
- Em C, não podemos declarar as variáveis na Expressão 1. Porém, pode ser uma exceção em alguns compiladores.
Exemplo 1
#include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)> Exemplo 2
#include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)> Propriedades da Expressão 2
- A expressão 2 é uma expressão condicional. Ele verifica se uma condição específica deve ser satisfeita. Caso contrário, o loop é encerrado.
- A expressão 2 pode ter mais de uma condição. No entanto, o loop irá iterar até que a última condição se torne falsa. Outras condições serão tratadas como declarações.
- A expressão 2 é opcional.
- A expressão 2 pode realizar a tarefa da expressão 1 e da expressão 3. Ou seja, podemos inicializar a variável, bem como atualizar a variável de loop na própria expressão 2.
- Podemos passar um valor zero ou diferente de zero na expressão 2. Porém, em C, qualquer valor diferente de zero é verdadeiro e zero é falso por padrão.
Exemplo 1
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)> Exemplo 2
#include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\\'%d %d %d
\\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)> Exemplo 3
strsep c
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } Saída
listando java
infinite loop
Propriedades da Expressão 3 - A expressão 3 é usada para atualizar a variável do loop.
- Podemos atualizar mais de uma variável ao mesmo tempo.
- A expressão 3 é opcional.
Exemplo 1
#include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)> Corpo de laço
As chaves {} são usadas para definir o escopo do loop. No entanto, se o loop contiver apenas uma instrução, não precisaremos usar colchetes. Um loop sem corpo é possível. As chaves funcionam como separadores de blocos, ou seja, a variável de valor declarada dentro do loop for é válida apenas para aquele bloco e não fora dele. Considere o seguinte exemplo.
#include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)> Infinitivo para loop em C
Para tornar um loop for infinito, não precisamos fornecer nenhuma expressão na sintaxe. Em vez disso, precisamos fornecer dois pontos e vírgulas para validar a sintaxe do loop for. Isso funcionará como um loop for infinito.
#include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } Se você executar este programa, verá a declaração acima infinitas vezes.
