Uma matriz é uma coleção homogênea de tipos semelhantes de elementos que possuem uma localização de memória contígua.
Uma matriz é um tipo de dados definido pelo usuário.
Um array é um tipo de estrutura de dados onde armazenamos os elementos de um tipo de dados semelhante. Em um array, podemos armazenar apenas um conjunto fixo de elementos. Também podemos usá-lo como um objeto.
O array é um armazenamento baseado em índice, onde o primeiro elemento é armazenado no índice 0. A estrutura abaixo ajuda a entender a estrutura de um array.
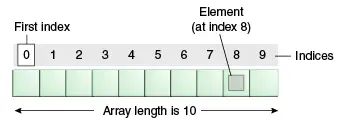
Características de uma matriz
- Uma matriz armazena elementos que possuem o mesmo tipo de dados.
- Elementos da matriz armazenados em locais de memória contíguos.
- O armazenamento de elementos de array 2-D é linha por linha em um local de memória contíguo.
- O nome da matriz representa o endereço do elemento inicial.
- O tamanho de um array deve ser inicializado no momento da declaração.
- O tamanho do array deve ser uma expressão constante e não uma variável.
- Podemos recuperar elementos do array especificando o valor de índice correspondente do elemento.
Vantagem
Otimização de código: Um array ajuda a otimizar o código, o que aumenta a velocidade e o desempenho do programa. Isso nos permite recuperar ou classificar os dados do array com mais eficiência.
Acesso aleatório: Ele fornece a capacidade de acessar qualquer dado de um array em tempo constante (independentemente de sua posição e tamanho). Assim, podemos obter diretamente quaisquer dados de um array localizado em qualquer posição do índice.
Desvantagem
Limite de tamanho: Um array nos permite armazenar apenas um número fixo de elementos. Uma vez declarado o array, não podemos alterar seu tamanho. Portanto, se quisermos inserir mais elementos do que o declarado, não é possível.
Declaração de matriz
Assim como o JavaScript, o TypeScript também oferece suporte a arrays. Existem duas maneiras de declarar um array:
1. Usando colchetes.
let array_name[:datatype] = [val1,val2,valn..]
Exemplo:
let fruits: string[] = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
2. Usando um tipo de array genérico.
converter string em char java
let array_name: Array = [val1,val2,valn..]
Exemplo:
let fruits: Array = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
Tipos de array em TypeScript
Existem dois tipos de matriz:
- Matriz Unidimensional
- Matriz Multidimensional

Matriz Unidimensional
Uma matriz unidimensional é um tipo de matriz linear que contém apenas uma linha para armazenar dados. Possui um único conjunto de colchetes ('[]'). Podemos acessar seus elementos usando índice de linha ou coluna.
Sintaxe
let array_name[:datatype];
Inicialização
array_name = [val1,val2,valn..]
Exemplo
let arr:number[]; arr = [1, 2, 3, 4] console.log('Array[0]: ' +arr[0]); console.log('Array[1]: ' +arr[1]);
Saída:
Array[0]: 1 Array[1]: 2
Matriz Multidimensional
Uma matriz multidimensional é uma matriz que contém uma ou mais matrizes. Na matriz multidimensional, os dados são armazenados em um índice baseado em linha e coluna (também conhecido como formato de matriz). Uma matriz bidimensional (matriz 2-D) é a forma mais simples de uma matriz multidimensional.

Sintaxe
let arr_name:datatype[][] = [ [a1,a2,a3], [b1,b2,b3] ];
Inicialização
let arr_name:datatype[initial_array_index][referenced_array_index] = [ [val1,val2,val 3], [v1,v2,v3]];
Exemplo
var mArray:number[][] = [[1,2,3],[5,6,7]] ; console.log(mArray[0][0]); console.log(mArray[0][1]); console.log(mArray[0][2]); console.log(); console.log(mArray[1][0]); console.log(mArray[1][1]); console.log(mArray[1][2]);
Saída:
1 2 3 5 6 7
Objeto de matriz
Objetos array nos permitem armazenar vários valores em uma única variável. Podemos criar um array usando o objeto Array. O construtor Array é usado para passar os seguintes argumentos para criação de array.
- Um valor numérico que representa o tamanho de uma matriz ou
- Uma lista de valores separados por vírgula.
Sintaxe
let arr_name:datatype[] = new Array(values);
Exemplo
//array by using the Array object. let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint','2200','Java','Abhishek'); for(var i = 0;i <arr.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2200 Java Abhishek </pre> <h3>Array Traversal by using a for...in loop</h3> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let i:any; let arr:string[] = ['JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek']; for(i in arr) { console.log(arr[i]) } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <h3>Passing Arrays to Functions</h3> <p>We can pass arrays to functions by specifying the array name without an index.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek'); //Passing arrays in function function display(arr_values:string[]) { for(let i = 0;i <arr_values.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } calling arrays in function display(arr); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <hr> <h2>TypeScript Spread operator</h2> <p>The spread operator is used to initialize arrays and objects from another array or object. We can also use it for object de-structuring. It is a part of the ES 6 version.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray); </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6 </pre> <hr> <h2>Array Methods</h2> <p>The list of array methods with their description is given below.</p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>SN</th> <th>Method</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> <tr> <td>1.</td> <td>concat()</td> <td>It is used to joins two arrays and returns the combined result.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2.</td> <td>copyWithin()</td> <td>It copies a sequence of an element within the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3.</td> <td>every()</td> <td>It returns true if every element in the array satisfies the provided testing function.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>4.</td> <td>fill()</td> <td>It fills an array with a static value from the specified start to end index.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.</td> <td>indexOf()</td> <td>It returns the index of the matching element in the array, otherwise -1.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>6.</td> <td>includes()</td> <td>It is used to check whether the array contains a certain element or not.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>7.</td> <td>Join()</td> <td>It is used to joins all elements of an array into a string.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>8.</td> <td>lastIndexOf()</td> <td>It returns the last index of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>9.</td> <td>Pop()</td> <td>It is used to removes the last elements of the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>10.</td> <td>Push()</td> <td>It is used to add new elements to the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>11.</td> <td>reverse()</td> <td>It is used to reverse the order of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>12.</td> <td>Shift()</td> <td>It is used to removes and returns the first element of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>13.</td> <td>slice()</td> <td>It returns the section fo an array in the new array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>14.</td> <td>sort()</td> <td>It is used to sort the elements of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>15.</td> <td>splice()</td> <td>It is used to add or remove the elements from an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>16.</td> <td>toString()</td> <td>It returns the string representation of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>17.</td> <td>unshift()</td> <td>It is used to add one or more elements to the beginning of an array.</td> </tr> </table></arr_values.length;i++)></pre></arr.length;i++)> Array Traversal usando um loop for...in
Exemplo
let i:any; let arr:string[] = ['JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek']; for(i in arr) { console.log(arr[i]) } Saída:
JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek
Passando arrays para funções
Podemos passar arrays para funções especificando o nome do array sem um índice.
Exemplo
anaconda vs cobra python
let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek'); //Passing arrays in function function display(arr_values:string[]) { for(let i = 0;i <arr_values.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } calling arrays in function display(arr); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <hr> <h2>TypeScript Spread operator</h2> <p>The spread operator is used to initialize arrays and objects from another array or object. We can also use it for object de-structuring. It is a part of the ES 6 version.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray); </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6 </pre> <hr> <h2>Array Methods</h2> <p>The list of array methods with their description is given below.</p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>SN</th> <th>Method</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> <tr> <td>1.</td> <td>concat()</td> <td>It is used to joins two arrays and returns the combined result.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2.</td> <td>copyWithin()</td> <td>It copies a sequence of an element within the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3.</td> <td>every()</td> <td>It returns true if every element in the array satisfies the provided testing function.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>4.</td> <td>fill()</td> <td>It fills an array with a static value from the specified start to end index.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.</td> <td>indexOf()</td> <td>It returns the index of the matching element in the array, otherwise -1.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>6.</td> <td>includes()</td> <td>It is used to check whether the array contains a certain element or not.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>7.</td> <td>Join()</td> <td>It is used to joins all elements of an array into a string.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>8.</td> <td>lastIndexOf()</td> <td>It returns the last index of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>9.</td> <td>Pop()</td> <td>It is used to removes the last elements of the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>10.</td> <td>Push()</td> <td>It is used to add new elements to the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>11.</td> <td>reverse()</td> <td>It is used to reverse the order of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>12.</td> <td>Shift()</td> <td>It is used to removes and returns the first element of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>13.</td> <td>slice()</td> <td>It returns the section fo an array in the new array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>14.</td> <td>sort()</td> <td>It is used to sort the elements of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>15.</td> <td>splice()</td> <td>It is used to add or remove the elements from an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>16.</td> <td>toString()</td> <td>It returns the string representation of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>17.</td> <td>unshift()</td> <td>It is used to add one or more elements to the beginning of an array.</td> </tr> </table></arr_values.length;i++)> Operador de propagação TypeScript
O operador spread é usado para inicializar arrays e objetos de outro array ou objeto. Também podemos usá-lo para desestruturação de objetos. Faz parte da versão ES 6.
Exemplo
let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray);
Saída:
CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6
Métodos de matriz
A lista de métodos de array com sua descrição é fornecida abaixo.
| SN | Método | Descrição |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | concat() | É usado para unir dois arrays e retornar o resultado combinado. |
| 2. | copiarDentro() | Ele copia uma sequência de um elemento dentro do array. |
| 3. | todo() | Ele retorna verdadeiro se cada elemento da matriz satisfizer a função de teste fornecida. |
| 4. | preencher() | Ele preenche uma matriz com um valor estático do índice inicial ao final especificado. |
| 5. | índice de() | Ele retorna o índice do elemento correspondente na matriz, caso contrário -1. |
| 6. | inclui() | É usado para verificar se o array contém um determinado elemento ou não. |
| 7. | Juntar() | É usado para unir todos os elementos de um array em uma string. |
| 8. | lastIndexOf() | Ele retorna o último índice de um elemento do array. |
| 9. | Pop() | É usado para remover os últimos elementos do array. |
| 10. | Empurrar() | É usado para adicionar novos elementos ao array. |
| onze. | reverter() | É usado para inverter a ordem de um elemento na matriz. |
| 12. | Mudança() | É usado para remover e retornar o primeiro elemento de um array. |
| 13. | fatiar() | Ele retorna a seção de um array no novo array. |
| 14. | organizar() | É usado para classificar os elementos de um array. |
| quinze. | emenda() | É usado para adicionar ou remover elementos de um array. |
| 16. | para sequenciar() | Ele retorna a representação em string de um array. |
| 17. | não mudar() | É usado para adicionar um ou mais elementos ao início de um array. |
