Nesta seção, aprenderemos como podemos ler dados de um arquivo Excel.
aes vs des
Em Java, a leitura de um arquivo Excel não é semelhante à leitura de um arquivo Word por causa das células no arquivo Excel. JDK não fornece API direta para ler ou escrever documentos do Microsoft Excel ou Word. Temos que contar com a biblioteca de terceiros que é o Apache POI.
O que é Apache POI?
Ponto de interesse do Apache (Poor Obfuscation Implementation) é uma API Java para ler e escrever documentos Microsoft em ambos os formatos .xls e .xlsx . Ele contém classes e interfaces. A biblioteca Apache POI fornece duas implementações para leitura de arquivos Excel:
Interfaces e classes no Apache POI
Interfaces
Aulas
Aulas XLS
Aulas XLSX
Etapas para ler dados do arquivo XLS
Passo 1: Crie um projeto Java simples no Eclipse.
Passo 2: Agora, crie uma pasta lib no projeto.
Etapa 3: Baixe e adicione os seguintes arquivos jar na pasta lib:
- commons-coleções4-4.1.jar Clique aqui
- poi-3.17.jar Clique aqui
- poi-ooxml-3.17.jar Clique aqui
- poi-ooxml-schemas-3.17.jar Clique aqui
- xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar Clique aqui
Passo 4: Defina o caminho da classe:
travessia de pré-encomenda de uma árvore
Clique com o botão direito no projeto -> Caminho de construção -> Adicionar JARs externos -> selecione todos os arquivos jar acima -> Aplicar e fechar.
Etapa 5: Agora crie um arquivo de classe com o nome LerExcelFileDemo e escreva o seguinte código no arquivo.
Etapa 6: Crie um arquivo Excel com o nome 'student.xls' e escreva alguns dados nele.
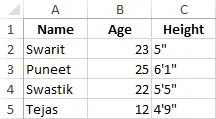
Etapa 7: Salve e execute o programa.
Exemplo de leitura de arquivo Excel (.xls)
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.FormulaEvaluator; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row; public class ReadExcelFileDemo { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { //obtaining input bytes from a file FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(new File('C:\demo\student.xls')); //creating workbook instance that refers to .xls file HSSFWorkbook wb=new HSSFWorkbook(fis); //creating a Sheet object to retrieve the object HSSFSheet sheet=wb.getSheetAt(0); //evaluating cell type FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator=wb.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator(); for(Row row: sheet) //iteration over row using for each loop { for(Cell cell: row) //iteration over cell using for each loop { switch(formulaEvaluator.evaluateInCell(cell).getCellType()) { case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: //field that represents numeric cell type //getting the value of the cell as a number System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue()+ ' '); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: //field that represents string cell type //getting the value of the cell as a string System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue()+ ' '); break; } } System.out.println(); } } } Saída:
Name Age Height Swarit 23.0 5' Puneet 25.0 6'1' Swastik 22.0 5'5' Tejas 12.0 4'9'
Lendo arquivo XLSX
Todas as etapas permanecerão as mesmas, exceto o formato do arquivo.
Mesa: funcionário.xslx
colher de chá vs colher de sopa

Exemplo de leitura de arquivo Excel (.xlsx)
Neste exemplo usamos a classe XSSFWorkbook.
codificação java instrução if else
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.util.Iterator; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook; public class XLSXReaderExample { public static void main(String[] args) { try { File file = new File('C:\demo\employee.xlsx'); //creating a new file instance FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); //obtaining bytes from the file //creating Workbook instance that refers to .xlsx file XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(fis); XSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0); //creating a Sheet object to retrieve object Iterator itr = sheet.iterator(); //iterating over excel file while (itr.hasNext()) { Row row = itr.next(); Iterator cellIterator = row.cellIterator(); //iterating over each column while (cellIterator.hasNext()) { Cell cell = cellIterator.next(); switch (cell.getCellType()) { case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: //field that represents string cell type System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + ' '); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: //field that represents number cell type System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + ' '); break; default: } } System.out.println(''); } } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } Saída:
Employee ID Employee Name Salary Designation Department 1223.0 Harsh 20000.0 Marketing Manager Marketing 3213.0 Vivek 15000.0 Financial Advisor Finance 6542.0 Krishna 21000.0 HR Manager HR 9213.0 Sarika 34000.0 Sales Manager Sales
Lendo um valor de célula específico de um arquivo Excel (.xlsx)
Mesa: EmployeeData.xlsx

Exemplo
No exemplo a seguir, lemos o valor de 2elinha e o 2ecoluna. A contagem de linhas e colunas começa em 0. Portanto, o programa retorna 'Engenheiro de Software'.

//reading value of a particular cell import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook; public class ReadCellExample { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadCellExample rc=new ReadCellExample(); //object of the class //reading the value of 2nd row and 2nd column String vOutput=rc.ReadCellData(2, 2); System.out.println(vOutput); } //method defined for reading a cell public String ReadCellData(int vRow, int vColumn) { String value=null; //variable for storing the cell value Workbook wb=null; //initialize Workbook null try { //reading data from a file in the form of bytes FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream('C:\demo\EmployeeData.xlsx'); //constructs an XSSFWorkbook object, by buffering the whole stream into the memory wb=new XSSFWorkbook(fis); } catch(FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch(IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } Sheet sheet=wb.getSheetAt(0); //getting the XSSFSheet object at given index Row row=sheet.getRow(vRow); //returns the logical row Cell cell=row.getCell(vColumn); //getting the cell representing the given column value=cell.getStringCellValue(); //getting cell value return value; //returns the cell value } } Saída:
Software Engineer
