Para realizar qualquer operação de entrada e saída em C++, precisamos usar arquivos de cabeçalho iostream. Sem um arquivo de cabeçalho, não podemos receber a entrada do usuário ou imprimir qualquer saída.
Sintaxe do arquivo de cabeçalho:
#include #include 'iostream.h'
Existem dois tipos de streams no arquivo de cabeçalho iostream
1. Fluxo de entrada : Para receber qualquer entrada do usuário, precisamos usar cin, que pertence ao fluxo de entrada
álgebra relacional em rdbms
Sintaxe para usar o fluxo de entrada:
std::cin>>variable_name
Quando o cin é executado, o cursor irá parar na instrução específica até que o valor seja inserido. O valor inserido será armazenado em uma variável.
2. Fluxo de saída : Para imprimir a saída, usamos funções integradas no fluxo de saída cout
Sintaxe para cout
std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p>When cout is executed, the value in the variable will be printed.</p> <h3>Different operations in iostream</h3> <p> <strong>1. Cin</strong> </p> <p>Using cin, we can take input from the user and store the value in the variable. We need to use the cin keyword followed by >> and the variable name.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax:</strong> </p> <pre> std::cin>>variable_name </pre> <p>To use cin, we need to use <strong>#include </strong> as cin belongs to this header file, and without this, an error will occur.</p> <p> <strong>Example code for cin:</strong> </p> <pre> //using header file iostream #include using namespace std; int main() { string name; //cin declaration cin >> name; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we used cin to take the input, so to use cin, we included header file. When the input is taken, the string input is stored in the name variable.</p> <p> <strong>2. Cout</strong> </p> <p>To print the output, we need to use the cout keyword, which belongs to the iostream header file. To use cout, we need to use the cout keyword followed by << and variable or the statement to print the output.</p> <p>The syntax for using cout:</p> <pre> std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p> <strong>Example of using cout:</strong> </p> <pre> //to use the cout statement, we need to use the iostream header file #include using namespace std; int main() { //cout statement is used here to print the statement cout << 'Hi from cout statement'; return 0;} </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-2.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> :</p> <p>In the above code, we used a cout statement to print the statement. To use the cout statement, we need to include iostream.h header file. Once the cout is executed, statement or variable value will be printing the output. To print any statement, we need to use double quotes (' '), and to print a variable value; we need to use just the variable name without double quotes(' ')</p> <p> <strong>3. Cerr</strong> </p> <p>Cerr is used to print errors in C++, which is present in the iostream header file. If we need to print any error message in the code if any condition fails, then cerr is very helpful.</p> <p>The syntax for cerr is:</p> <pre> cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<'the number entered in even number'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << 'enter proper number' '
'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<'the number entered is even enter a name'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << 'enter even number' '
'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></'the></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name> Para usar cin, precisamos usar #incluir como cin pertence a este arquivo de cabeçalho e, sem isso, ocorrerá um erro.
Código de exemplo para cin:
//using header file iostream #include using namespace std; int main() { string name; //cin declaration cin >> name; return 0; } Saída:
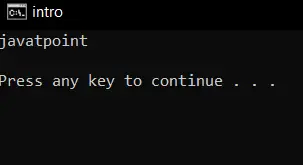
Explicação:
No código acima, usamos cin para receber a entrada, então para usar cin, incluímos o arquivo de cabeçalho. Quando a entrada é obtida, a entrada da string é armazenada na variável name.
2. Corte
Para imprimir a saída, precisamos usar a palavra-chave cout, que pertence ao arquivo de cabeçalho iostream. Para usar cout, precisamos usar a palavra-chave cout seguida de << e variável ou a instrução para imprimir a saída.
A sintaxe para usar cout:
std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p> <strong>Example of using cout:</strong> </p> <pre> //to use the cout statement, we need to use the iostream header file #include using namespace std; int main() { //cout statement is used here to print the statement cout << 'Hi from cout statement'; return 0;} </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-2.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> :</p> <p>In the above code, we used a cout statement to print the statement. To use the cout statement, we need to include iostream.h header file. Once the cout is executed, statement or variable value will be printing the output. To print any statement, we need to use double quotes (' '), and to print a variable value; we need to use just the variable name without double quotes(' ')</p> <p> <strong>3. Cerr</strong> </p> <p>Cerr is used to print errors in C++, which is present in the iostream header file. If we need to print any error message in the code if any condition fails, then cerr is very helpful.</p> <p>The syntax for cerr is:</p> <pre> cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered in even number\'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter proper number\' \'
\'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered is even enter a name\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter even number\' \'
\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></\'the></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name> Saída:

Explicação :
No código acima, usamos uma instrução cout para imprimir a instrução. Para usar a instrução cout, precisamos incluir o arquivo de cabeçalho iostream.h. Assim que o cout for executado, a instrução ou o valor da variável imprimirá a saída. Para imprimir qualquer instrução, precisamos usar aspas duplas (' ') e imprimir um valor variável; precisamos usar apenas o nome da variável sem aspas duplas(' ')
3. Certo
Cerr é usado para imprimir erros em C++, que está presente no arquivo de cabeçalho iostream. Se precisarmos imprimir alguma mensagem de erro no código se alguma condição falhar, então cerr é muito útil.
A sintaxe para cerr é:
cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered in even number\'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter proper number\' \'
\'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered is even enter a name\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter even number\' \'
\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></\'the></pre></variable_name> Saída:

Explicação:
No código acima, estamos imprimindo um erro. Para imprimir este erro, usamos cerr, que pertence ao arquivo de cabeçalho iostream. Antes de imprimir o erro, armazenamos o erro em um buffer.
Exemplo : Para todos os fluxos de entrada e saída
#include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\\'the number entered is even enter a name\\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \\'enter even number\\' \\'
\\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\\'the>